
Big Data and MES, what are the challenges for the industry of the future?
1/ What is Big Data?
Before talking about Big Data, it is important to know that today’s manufacturing industries put product quality at the heart of all manufacturing processes. This with a view to productivity and cost reduction.
To achieve this, they rely on new digital technologies: Internet of Things, cobotics, augmented reality, 3D printing or artificial intelligence.
Intelligent and interconnected automation requires machines to collect and share information. And it is the way in which these machines and the factory communicate via networks that characterises what is known as Industry 4.0.
Seamless connectivity of all the plant’s sensors and actuators, even those at remote sites, is possible using big data.
Through the dematerialisation of activities and the generalised interconnection of objects, machines and people, access is open to the collection and analysis of massive data in manufacturing plants.
This correlated data, coupled with predictive analysis, enables industrialists to supervise, control and pilot their installations. But also to anticipate malfunctions and reduce production tool downtime.
By integrating industrial solutions such as MES (Manufacturing Execution System) and Lean, manufacturers are guaranteed to reduce costs, increase productivity, ensure process reliability and improve quality.
Industry 4.0 is characterised by the interconnections between new digital technologies or their possibilities to communicate with each other.
2/ Big Data and MES
2.1 What is Big Data ?
By definition, Big Data means big data or massive data. It refers to a very large set of data that no conventional database or information management tool can really work with. It manifests itself through connected objects where data is generated from many and diverse sources such as equipment, people, infrastructure and intelligent sensors. The pooling of this data will make it possible to be more flexible and quicker in accessing information.
Moreover, the massive collection of information and the multiplication of technologies used raise questions about the security of this data in the face of multiple threats. For this reason, the implementation by industrialists of technical standards and methods is essential to guarantee optimal protection of their infrastructures.
Big Data is therefore a promising solution for the factory of the future enabling companies to improve their performance. However, before thinking about implementing it, the ground must be prepared by investing in the fundamentals represented, among others, by the MES.
2.2 What is MES ?
In this context, the MES offers multi-source and multi-media interconnectivity, a necessary basis for the digitalisation of industrial processes. Interfaced with all connected production means, the MES guides and reacts instantaneously to the workshop’s activities. It is the central point for all the execution data, responsible for transmitting the right information at the right time, both to the men (digitised work instructions, requested traceability, progress of OFs, etc.) and to the machines (start/stop, machining parameters, part status, etc.).
The MES creates this digital link missing from the industrial ecosystem.
It also ensures continuity between ERP data and workshop operations through a complete digital chain, from the creation of the Manufacturing Order (MO) to the final product.
By capitalising all production data in real time, the MES provides a view of the stock and output of the OFs with a granularity of around one minute.
For all these reasons, the MES is the complementary tool par excellence to the ERP.
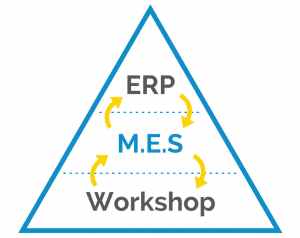
2.3 M.E.S Qualaxy
Infodream’s Qual@xy Suite, the MES developed by Infodream, is capable of exchanging data with most existing industrial systems via Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) or with connected instruments such as a screwdriver, hand shower, printer, etc.
For these exchanges, it uses standard communication protocols.
This short video shows that the torque and tightening angle of the screwdriver are automatically and instantaneously entered into the MES Qualaxy software.
3/ The 3 keys to a successful Big Data strategy
In production, there are numerous possibilities for using Big Data. It therefore makes sense to determine beforehand where to start. Here are three good practices for an effective approach:
3.1 Putting people at the centre
When it comes to collecting and analysing data, technology is obviously important. But in the end, the value of technology has a direct correlation with the skills of the people using the technology and analysing the data. This means that you may need to bring in people with the knowledge and mindset to tackle the challenges of Big Data, or ensure that the solution you choose will be able to provide meaningful data that is understandable to different users.
3.2 Define clear objectives
The most important question you should continually ask yourself when developing a strategy is: « what is our main objective? This question will help you determine what types of operations or data from the supply chain you will need to collect and analyse to achieve your objectives, and where to store them.
3.3 Start with an area where you have problems
Since there are many potential opportunities, it is not advisable to complicate matters. Start with problems that are obvious to correct (such as production losses for example) and for which you do not clearly understand the developments and causes.
