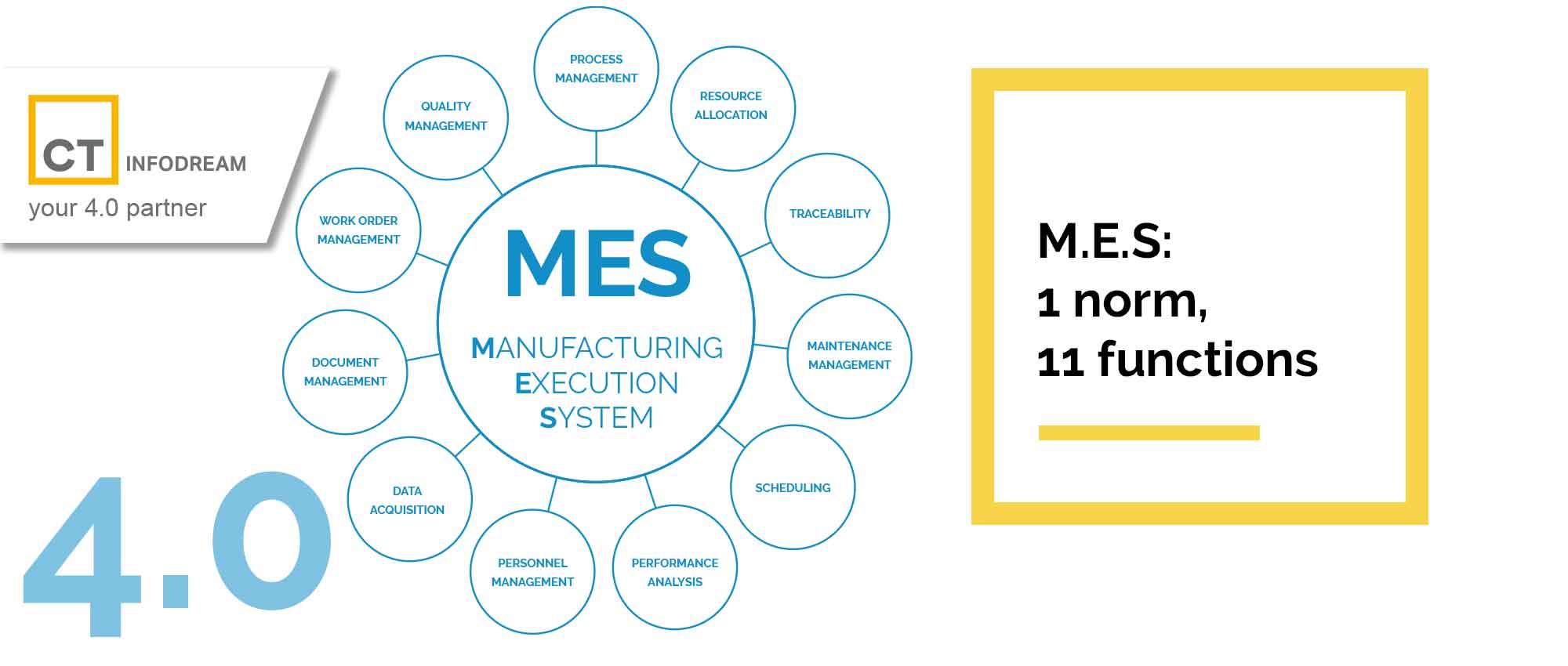
MES (Manufacturing Execution System): 1 standard, 11 functions
The 11 functions of the MES (Manufacturing Execution System) are defined by ISA95. This standard makes it possible to delimit the common coverage imposed on MES solutions.
In France, the MES Club is the association that guarantees the MES offers on the market.
The 11 functions of ISA-95 :
- Data acquisition
- Scheduling
- Personnel management
- Resource management
- Flow of products and batches
- Product traceability and genealogy
- Quality control
- Process management
- Performance analysis
- Document management
- Maintenance management
In order to create consistency in the offer, an MES software is not forced to fulfil the completeness of ISA95 functions. Some of these functions can be addressed by software solutions in their own right, such as scheduling with ERP or other specialised software.
Practical application of the MES functions
The specific details of each function may differ depending on the software system.
However, they should all share the following key points:
- Data collection and acquisition
Allow the input of all information during production, manually and/or automatically. - Scheduling
Provide a global view of the planned production orders and their production routing including electronic job cards. - Staff management
Manage the necessary skills and authorizations for people, products and/or operations. - Resource management
Define and track the status of each resource associated with producing the production unit (production tools, machines, breakdowns, material shortage, etc.). - Production tracking and dispatch
Manage the bidirectional flow of production data in real time between the ERP and the workshop. - Product traceability and genealogy
Associate a final part or batch with all its manufacturing data from the raw material to the component assembly. - Quality management
Manage the quality of manufacturing processes and units including quality deviations and exceptions. This function can be integrated directly into the MES software or can use external software such as SPC software and NCMS (non-conformance management system). - Process management
Provide process routing and operational sequencing including full traceability. - Performance analysis
Consolidate data to calculate the key performance indicators such as Right first time (RFT), Rework, Scrap, Process capability (Cpk), Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), Opportunities, etc. - Document management
Make available to the operator at the correct time the documents (instructions, drawings, notes) necessary to carry out their work. - Maintenance management
Optimize the planning of preventive maintenance operations to reduce the impact on manufacturing.
All of these functions occur at different levels of the workshop to meet the needs of each stakeholder in the production process.
Find out what the MES can do for your profession